03 Physical Well-being
Highlights:
1. Indicators for measuring physical health and their implications
Problem
Measuring
Tool
Indicator
Abnormal growth and
development
Weight (kg) and Height
(cm)
Scale, measuring
tape
- Growth charts
Obesity
Weight (kg) /Height (m)²
Scale, measuring
tape
- Body Mass Index (BMI)
Fat ratio
Calipers / body fat
scale
- Fat ratio
Central obesity
Waist Circumference
(cm)
Measuring tape
- Waist circumference
Waist / Hip
Circumference (cm)
Measuring tape
- Waist-hip ratio (WHR)
Cardiovascular diseases such as
heart diseases and hypertension
Pulse rate
Counting Heart rate
monitor
- Pulse rate
Blood Pressure
Blood Pressure
Monitor
- Systolic blood pressure
- Diastolic blood pressure
2. Aspects of Physical Fitness
Aspect
Examples
Muscular strength
Resistance exercise such as weight lifting
Muscular endurance
Marathon
Cardio-respiratory endurance
Aerobic exercise
Flexibility
Stretching, Tai-chi, Yoga
3. Individual Level
Healthy Diet
Nutrition
- Macro-nutrients – for growth, metabolic function and bodybuilding
- Protein
- Carbo-hydrate
- Fat (lipids)
- Micro-nutrients – for regulating cell function
- Vitamins – fat-soluble (vitamins A, D, E and K) and water-soluble (vitamins B and C)
- Minerals – include calcium, iron, phosphorus, sodium, potassium, magnesium and sulphur
Malnutrition
- Deficiency in nutrients / lack of particular nutrient in food
- Deficiency of vitamin C may cause scurvy
- Excess of nutrients
- Excessive intake of carbohydrates/ fat may lead to obesity
Unbalanced diet
- Low vegetable/ fibre diets
- increase the risk of colon cancer
- High fat, high salt and high sugar
- increase the risk of hypertension/ heart diseases
- Trans fatty acid
- increased risk of Coronary Heart Disease
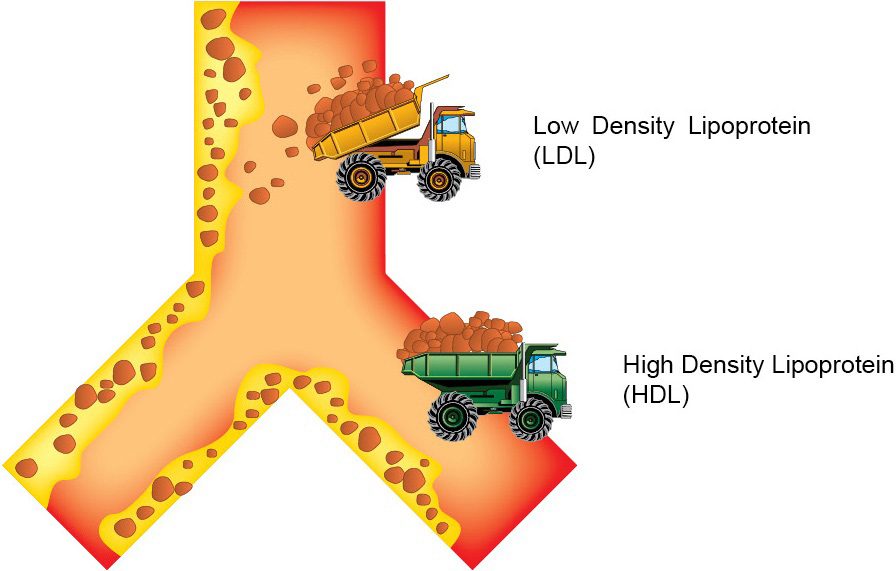
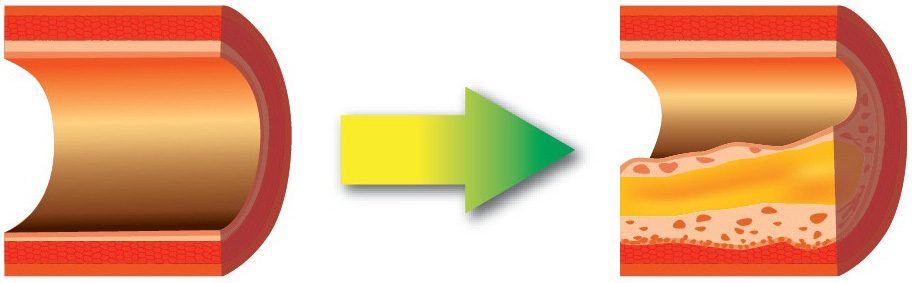
4. Cholesterol
- Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) – Bad Cholesterol
- High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) – Good Cholesterol
5. Eating Disorders
- Bulimia nervosa
- Anorexia nervosa (Online Survey : Am I having a Tendency of Getting Eating Disorders? )
6. Energy Balance
- Energy input vs energy output = weight gain / lose
- Unhealthy eating habits, such as the frequent consumption of high-calorie fast food, may lead to high energy input
- Insufficient physical activities due to the increasing sedentary nature of workplace and leisure activities, may lead to low energy output
- Obesity developed when energy input is much larger than the energy output
7. Health maintenance and disease prevention
Personal role
Protective factors
physical activities, recreation and rest, balanced diet,
good hygiene practices, protective measures (e.g.
helmets, seat-belts), universal precautions
Risk factors
drug abuse, inadequate physical activities/rest, unbalanced diet, non-hygienic practices , harmful/unsafe practices , a sedentary lifestyle
Society Role
- the role of government in health maintenance
- the collection and application of data in health protection of the citizens
Reading:
Application:
Assessing my learning
- What does a healthy body mean?
- How can an individual’s physical health be measured?
- How can we maintain a healthy body?










